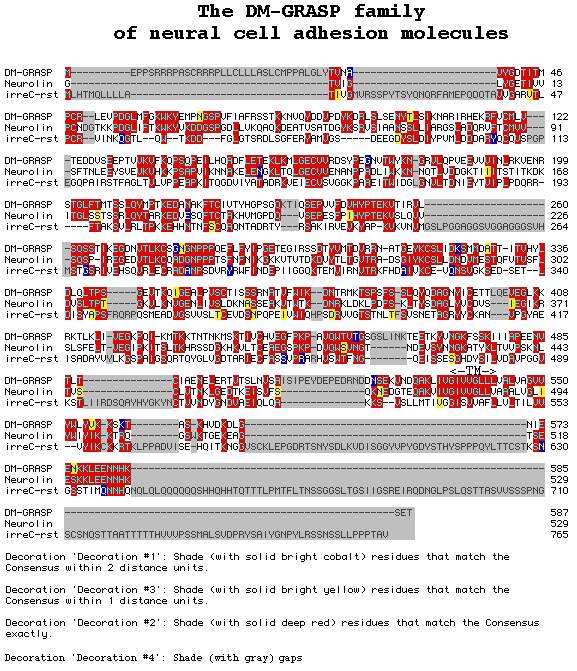
The similarity of the IrreC-rst protein to its vertebrate relatives is best in the extracellular domain (with the exception of the N-terminal region). TM denotes the transmembrane domains. Assuming a more primitive structure of the IrreC-rst protein, the intracellular domains of the vertebrate molecules might have evolved by several deletions.
DM-GRASP sequence (chicken) from:
Burns, F.R., Von Kannen, S., Guy, L., Raper, J.A., Kamholz, J., and Chang, S. (1991). DM-GRASP, a novel immunoglobulin superfamily axonal surface protein that supports neurite extension. Neuron 7, 209-220
Neurolin sequence (goldfish) from:
Laessing, U., Giordano, S., Stecher, B., Lottspeich, F., and Stuermer, C.A.O. (1994). Molecular characterization of fish neurolin: a growth-associated cell surface protein and member of the immunoglobulin superfamily in the fish retinotectal system with similarities to chick protein DM-GRASP/SC-1/BEN. Differentiation 56, 21-29
IrreC-rst sequence (Drosophila) from:
Ramos, R.G.P., Igloi, G.L., Lichte, B., Baumann, U., Maier, D., Schneider, T., Brandstätter, J.H., Fröhlich, A., and Fischbach, K.-F. (1993). The irregular chiasm C - roughest locus of Drosophila, which affects axonal projections and programmed cell death, encodes a novel immunoglobulin-like protein. Genes and Development 7, 2533-2547